Lung diseases are a significant global health concern, affecting millions of people and leading to severe consequences if not properly managed. The lungs are vital organs responsible for breathing, supplying oxygen to the blood, and removing carbon dioxide from the body. When lung function is compromised, it can impact overall health, quality of life, and longevity. This blog will explore the causes, symptoms, and prevention of common lung diseases, emphasizing the importance of early detection and proactive healthcare.
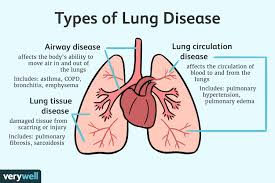
Common Types of Lung Diseases
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD is a progressive lung disease that includes conditions such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It is characterized by long-term breathing difficulties due to airway obstruction and inflammation. Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, although long-term exposure to pollutants, dust, and chemicals can also contribute. - Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition that causes the airways to narrow and swell, leading to breathing difficulties. It often triggers wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Asthma can be managed with medication and by avoiding triggers like allergens, smoke, and cold air. - Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Symptoms include cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening, particularly in infants, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. - Pulmonary Fibrosis
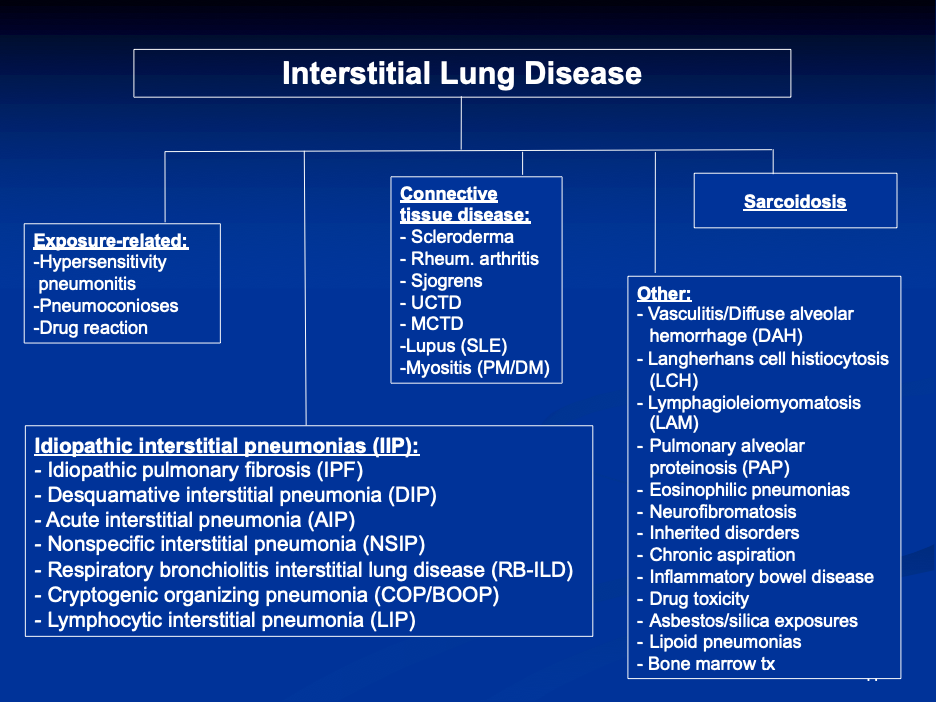
Pulmonary fibrosis involves the thickening and scarring of lung tissue, leading to progressive and irreversible lung damage. This condition results in shortness of breath, chronic dry cough, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. The cause is often unknown, but exposure to environmental toxins, certain medications, and radiation therapy can be contributing factors. - Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most deadly forms of cancer, often associated with smoking, though non-smokers can also develop the disease. Symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, hoarseness, weight loss, and coughing up blood. Early detection through screening can significantly improve survival rates.
Causes and Risk Factors

Several factors can increase the risk of developing lung diseases, including:
- Smoking: The leading cause of many lung diseases, including COPD and lung cancer.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to pollutants, both indoors and outdoors, can damage the lungs.
- Occupational Hazards: Exposure to asbestos, coal dust, and other industrial pollutants can lead to lung disease.
- Genetics: A family history of lung disease can increase the likelihood of developing conditions such as asthma and pulmonary fibrosis.
- Infections: Viral and bacterial infections can cause diseases like pneumonia, which may lead to chronic lung conditions.
Symptoms to Watch For
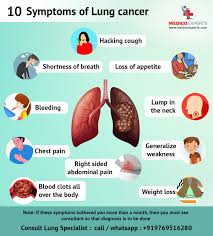
Common symptoms of lung diseases include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Wheezing or whistling sound when breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Chronic mucus production
- Fatigue or feeling unusually tired
It is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, particularly if they persist or worsen over time.
Prevention and Management
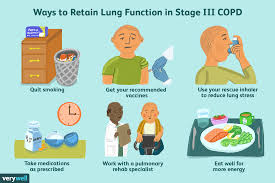
Preventing lung diseases involves making lifestyle changes and avoiding risk factors:
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the most effective way to protect your lung health.
- Avoid Pollutants: Minimize exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution by using air purifiers, wearing masks, and avoiding areas with high pollution levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity strengthens the lungs and improves respiratory health.
- Vaccinations: Vaccines can prevent infections like the flu and pneumonia, which can lead to lung complications.
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection of lung diseases through regular medical check-ups can lead to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Lung diseases are serious conditions that require attention and care. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures can help you take control of your lung health. By making informed lifestyle choices and seeking timely medical advice, you can protect your lungs and maintain a better quality of life. Always prioritize your respiratory health, as it is crucial to your overall well-being.



Leave a Reply